Reciprocal Depression in aVL: The Case for Serial ECGs
ECG Weekly Workout with Dr. Amal Mattu
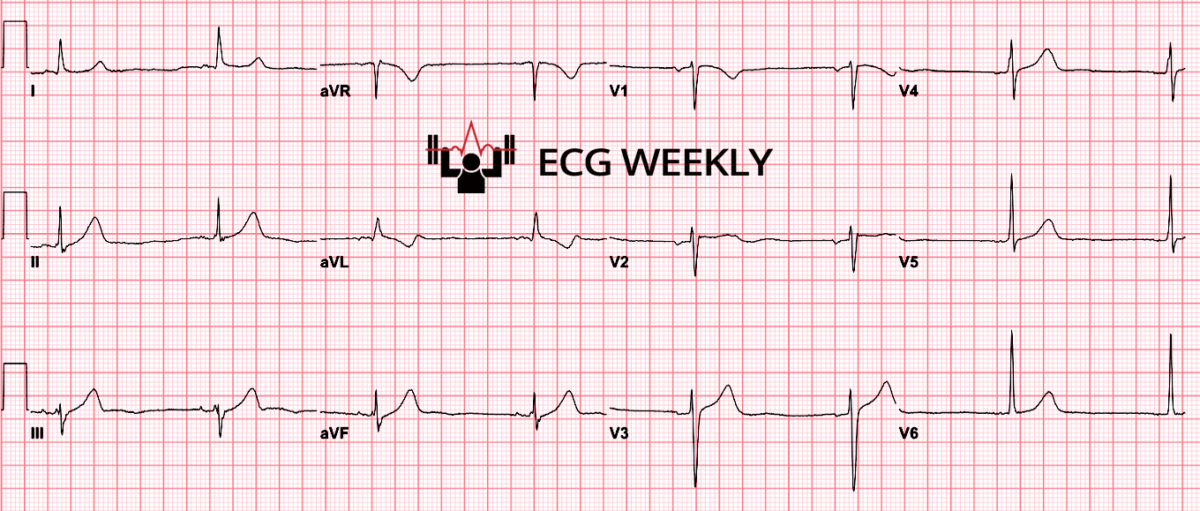
HPI
A 62-year-old man presents to the emergency department with acute chest pain associated with diaphoresis. He has cardiac risk factors including tobacco use. An initial 12-lead ECG is obtained on arrival and is read by the computer as non-acute with no clear ST elevation meeting STEMI criteria. Symptoms persist, and the treating team decides to obtain serial ECGs.
Before watching this week’s workout, review the arrival ECG carefully and consider:
-
- What abnormal finding in aVL should raise concern in a patient with chest pain and diaphoresis, even if there is no obvious ST elevation?
- What is the most appropriate immediate plan after seeing that finding: level of monitoring, repeat ECG strategy, and timing?
- If the initial tracing does not meet STEMI criteria, what change on a repeat ECG would confirm that this was not a “reassuring” first ECG?