2024 EM Boards ECG Review (Part I/II)
Emergency Medicine Board Review: Must Know ECGs with Dr. Amal Mattu
HPI
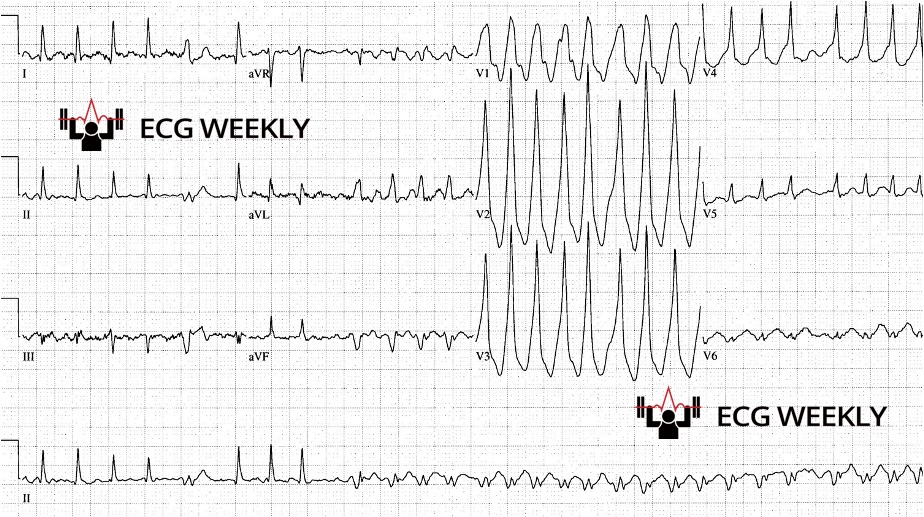
A 61-year-old man with a history of atrial fibrillation presents to ABEM general hospital with lightheadedness and palpitations. He is tachycardic but otherwise has normal vital signs. The following ECG is obtained:
Before watching the video, ask yourself:
-
-
- What is the heart rate and rhythm?
- What is the safest initial treatment option?
- How would your management change in treating stable vs. unstable patients with this rhythm?
-
Video
Kudos
Thanks to Drs. Nicolás Pineda and Alaa Nasr for sharing their cases this week!Are you preparing for the EM In-training (ITE) or qualifying exam exam? We can help!
Check out our collection of ECG Weekly Board Review Episodes, then look up the pertinent topics on ECG STAT to reinforce your learning. Lastly, you can test your retention with our new EM Board Review ECG skills exam on ECG Skills.
Summary of board review cases covered in this week’s episode:
Case 1: 61-year-old man with lightheadedness. 
- ECG Findings: Wide complex, irregularly irregular tachydysrhythmia with ventricular rate reaching rates of up to 300 bpm. QRS complexes have changing shapes and morphologies.
- Diagnosis: Atrial fibrillation with WPW
- Learning Points:
- Consider atrial fibrillation with WPW in all wide complex irregular tachycardias.
- Dangerous rhythm where misdiagnosis or treatment with any AV nodal blocker can be deadly!
- Avoid all AV nodal blockers, cardiovert any unstable patients and use procainamide if stable.
Case 2: 38-year-old man who works as a truck driver presents with palpitations and is found to have SVT. The following ECG is post conversion back to normal sinus rhythm:

- ECG Findings: Right axis deviation, SIQ3T3
- Diagnosis: Acute pulmonary embolism
- Learning Points:
- Always consider PE in any patient with right axis deviation (deep S wave in lead I)
- Consider the other important causes of RAD:
-
- Hyperkalemia
- Sodium channel blocker toxicity
- Pulmonary embolism
-
Case 3: 60-year-old man presents with dyspnea.

- ECG Findings: Narrow complex irregular tachycardia with multiple different P wave morphologies.
- Diagnosis: Multifocal atrial tachycardia
- Learning Points:
- Remember the differential diagnoses for narrow complex irregular tachycardias:
-
- Atrial fibrillation
- Atrial flutter with variable conduction
- Multifocal atrial tachycardia
-
- Never shock MAT, treat the underlying cause
- Board question prompt will commonly reference a patient with chronic pulmonary disease
- Remember the differential diagnoses for narrow complex irregular tachycardias:
Case 4: 55-year-old man with chest pain.

- ECG Findings: Diffuse ST segment elevation (except for V1/aVR), PR segment depression
- Diagnosis: Acute pericarditis
- Learning Points:
- Consider the following important differentials for chest pain on exams:
-
- Acute coronary syndrome
- Pulmonary embolism
- Aortic dissection
- Pericarditis/myocarditis
-
- Consider the following important differentials for chest pain on exams:
- Presence of ST segment depression (reciprocal changes) in any lead aside from leads V1 and aVR rules out pericarditis
- STEMIs do not generally produce tachycardia without cardiogenic shock
Case 5: 61-year-old woman with chest pain.

- ECG Findings: Biphasic T waves in leads V2 & V3
- Diagnosis: Wellens syndrome
- Learning Points:
- Highly predictive of proximal LAD lesion
- T waves may be deeply inverted or biphasic in mid-precordial leads (V2-V4)
- Patients may be pain free with normal troponins
Case 6: 50-year-old woman with lightheadedness.

- ECG Findings: Ventricular rate of ~84 bpm with lonely P waves
- Diagnosis: Slow progressive 2nd degree AV block, Mobitz I (Wenckeback)
- Learning Point:
- Emergency treatment is based on the ventricular rate, not the atrial rate or the type of AV block