Narrow QRS
Results:
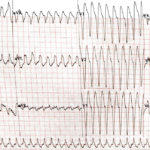
Preexcitation Pitfalls (Part 2): Wide, Regular, Fast…Treat It Like VT
A young man with recurrent palpitations presents to the emergency department hemodynamically stable during an episode. The arrival ECG shows a wide complex, regular tachycardia and the computer interpretation calls…
WPW with Orthodromic SVT (Orthodromic AVRT)
Key Points: Orthodromic AVRT is the most common tachyarrhythmia in WPW and presents as a regular narrow-complex SVT that is indistinguishable from AVNRT during the tachycardia. Mechanism: antegrade conduction down…
Premature Atrial Complexes (PACs)
Key Points PACs are early atrial depolarizations from an ectopic focus that create a premature P wave with a different morphology and axis than the sinus P wave, usually followed…
Unstable Bradyarrhythmias
Key Points: Unstable bradyarrhythmias cause poor perfusion which can rapidly progress to shock, irreversible organ injury, or cardiac arrest. Priority: Do not treat the heart rate alone — treat clinical…
Unstable Tachyarrhythmias
Key Points: Intervene Immediately: Unstable tachyarrhythmias pose significant risk for rapid clinical deterioration that may lead to irreversible end-organ damage or cardiac arrest. Clinical Indicators of Instability: Altered Mental Status:…
Premature Junctional Complexes (PJCs)
Key Points PJCs are premature impulses from ectopic foci in or near the AV junction. ECG hallmark is a narrow premature beat with an absent or retrograde P wave. Retrograde…
Premature Complexes (PACs, PJCs, & PVCs) Overview
Key Points: Premature complexes are early depolarizations arising from the atrium, AV junction, or ventricle which interrupt the expected sinus rhythm. Rapid classification by origin: look for a P wave…
Atrioventricular Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT)
Key Points: AVNRT is a paroxysmal, regular, usually narrow-complex SVT caused by a reentry circuit within or adjacent to the AV node. Dual-pathway physiology is typical. Bedside hallmark is a…
Atrioventricular Reciprocating Tachycardia (AVRT)
Key Points: AVRT is a re-entrant SVT that requires two limbs: the AV node and an accessory pathway. It is an AV node dependent tachycardia. Orthodromic AVRT conducts antegrade down…
Atrioventricular Blocks (AVB): Comprehensive Summary
Key Points: AV block specifically reflects delayed or failed impulse conduction from atria to ventricles. Classification of blocks depend on the location of conduction delay or block within the cardiac…
Narrow QRS Bradycardia: DDx
Key Point Narrow QRS bradycardias are often related to vagal tone or reversible causes, but not always benign. Certain AV blocks and conduction abnormalities may still carry significant risk, even…
Heart Rate & Rhythm Interpretation
Key Points: Treat the patient, not just the number or rhythm. Start with a 10-second stability check. If the rhythm explains hypotension, shock, ischemic chest pain, altered mentation, or severe…
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT)
Key Points Definition: Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) is a rare type of irregularly irregular supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) characterized by the presence of at least three or more different P wave…
Supraventricular Tachycardias (SVTs)
Key Points Definition: SVT refers to any tachyarrhythmia that originates above the ventricles (atria, AV node, or bundle of His). Most present as regular narrow-complex tachycardias, although aberrant conduction can…
Narrow & Irregular Tachycardia: DDx
Key Points Narrow irregular tachycardia = QRS <120 ms with variable R–R interval. The big three DDx: Atrial fibrillation (AF) with RVR, atrial flutter with variable block, multifocal atrial tachycardia…
Narrow & Regular Tachycardia: DDx
Key Points Narrow regular tachycardia = QRS <120 ms with a steady R–R interval. The big three DDx: sinus tachycardia, SVT (AVNRT/AVRT/junctional), and atrial flutter with fixed AV conduction (commonly…
Junctional Tachycardia
Key Points Origin: Junctional tachycardia is a rare type of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) that originates from the AV node or the bundle of His. Mechanism: The arrhythmia is caused…
ECG Tags
- A-Z
- ACS Mimics
- ACS-OMI
- Activation
- Advanced Level Curriculum
- Annual ECG Competition
- Anterior OMI
- Anterior STEMI
- Approach
- Arrest
- Arrhythmia
- Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy
- Artifact
- ARVC
- ARVD
- Atrial Parasystole
- Attending
- AV Block
- aVF
- aVL
- aVR
- Axis
- Basics
- Board Review
- Bradyarrhythmia
- Chest Pain
- Clumped Beats
- Conduction
- Core
- Core Level Curriculum
- Critical ECG Patterns
- Curriculum
- DDx
- Delta
- Devices
- Diagonal Branch Occlusion
- Differential Diagnoses
- Diffuse ST Elevation
- Documentation
- Early Repolarization
- ECG Interpretation
- ECG Localization
- ECG Variant
- Education/Teaching
- Electrolytes
- Emergencies
- Emergent Cath Lab Activation
- EMS
- Expert Level Curriculum
- Foundations Level Curriculum
- Guidelines
- High-Lateral STEMI
- Hub
- Hyperacute T waves
- Hypercalcemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypermagnesemia
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypokalemia
- Hypomagnesemia
- Hyponatremia
- Hypothermia
- I
- II
- Index
- Inferior OMI
- Inferior STEMI
- Intervals
- Irregular
- Ischemia
- Ischemia & Infarction
- J Waves
- JT
- Juvenile T wave
- LAD Occlusion
- Lateral STEMI
- LBBB
- LCx Occlusion
- Lead Placement
- Life Savers
- LV an
- LV Aneurysm
- Mastery Level Curriculum
- Metabolic
- Mimics
- Morphology
- Narrow QRS
- Occlusion MI
- OMI Pattern
- Orthodromic AVRT
- Osborn Waves
- P Wave
- Paced Rhythms
- Pacemaker/ICD
- Paramedics
- Pauses
- PE
- Pediatrics
- Pericardial
- Pericarditis
- PGY-1
- PGY-2
- PGY-3
- PGY-4
- Post-Cardiac Arrest
- Posterior Extension
- Posterior MI
- Posterior STEMI
- PR
- Preexcitation
- Premature Complexes
- Prolonged QT
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Pulse-Tapping Artifact
- PVCs
- Q Wave
- QRS
- QT
- R Waves
- RAD
- Rate
- RBBB
- RCA Occlusion
- Regular
- Reperfusion
- Rhythm
- RR
- S Waves
- Segments
- Seizure
- Serial ECGs
- Sgarbossa
- Shock
- ST
- ST Depression
- ST Elevation
- STEMI
- STEMI Equivalent
- STEMI Mimics
- STEMI Negative OMI
- Stepwise
- Stroke
- Structural
- Students
- SVT
- Syncope
- T Wave Inversion
- T Waves
- Tachyarrhythmia
- Tachycardia
- Tamponade
- Terminal QRS Distortion
- Toxicology
- TP
- Traditional STEMI Criteria
- U Waves
- Unstable
- V1-V4
- V5
- V6
- Vectors
- Ventricular Repolarization
- Ventricular Rhythms
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Voltage
- Waveforms
- Wide QRS
- Workflow
- WPW