Conduction
Results:
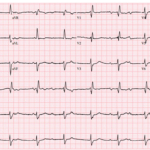
The Syncope ECG With Too Much P
A 68-year-old man has syncope, then has a second syncopal episode while lying still on a stretcher during evaluation at an outpatient clinic. He is sent emergently to the ED….
Preexcitation Pitfalls (Part 3): Wide, Irregular, Fast…Avoid AV Nodal Blockers
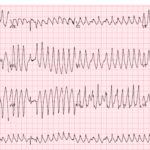
A 53-year-old man presents with palpitations and lightheadedness. The following ECG is obtained on arrival and appears very rapid and irregular with changing QRS morphologies. He starts showing signs of…
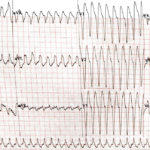
Preexcitation Pitfalls (Part 2): Wide, Regular, Fast…Treat It Like VT
A young man with recurrent palpitations presents to the emergency department hemodynamically stable during an episode. The arrival ECG shows a wide complex, regular tachycardia and the computer interpretation calls…
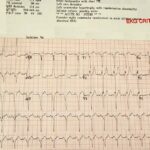
Too Many P Waves (P:QRS>1): DDx
Key Points: Non-conducted P waves (too many P waves) occur when atrial impulses fail to conduct to the ventricles. Automated ECG interpretations are unreliable in irregular rhythms and with non-conducted…
Preexcitation Pitfalls (Part 1): The “Inferior STEMI” That Isn’t
A critically ill 38-year-old man presents hypotensive, pale, and diaphoretic with abdominal pain and rectal bleeding. Upright chest X-ray shows free air under the diaphragm, and the patient is headed…
ECG Foundations: Vectors, Leads, & Activation
Key Points: An ECG records voltage differences over time. The ECG tracing is a plot where the horizontal axis is time and the vertical axis is voltage. Leads are viewpoints….
Third-Degree AV Block (Complete Heart Block)
Key Points: Definition: Third-degree AV block is complete failure of conduction from atria to ventricles, resulting in independent atrial and ventricular activity—known as AV dissociation. Hallmark Feature: No P waves…
Second-Degree AV Block Type I (Mobitz I/Wenckebach)
Key Points: Definition: Progressive PR interval prolongation until one atrial impulse fails to conduct to the ventricles (P wave is non-conducted), after which the cycle repeats. Site of Block: Typically…
Second-Degree AV Block with 2:1 Conduction
Key Points: Definition: A form of second-degree AV block in which every other atrial impulse is blocked, producing a 2:1 atrioventricular conduction ratio. Typing Limitation: Differentiating between Mobitz I and…
High-Grade (Advanced) AV Block
Key Points: Definition: A severe form of second-degree AV block with two or more consecutive non‑conducted P waves (for example 3:1, 4:1). Do not force a Mobitz label when multiple…
Dr. Mattu’s 5 Favorite ECG Cases of 2025
A 68-year-old man presents after syncope with profound bradycardia. The ECG shows a very slow ventricular rate with high-grade AV block. The reflex move is to focus only on pacing,…
New RBBB and LAFB (Bifascicular Block) in ACS
Key Points Think proximal LAD / septal ischemia until proven otherwise when a patient with ischemic symptoms develops new RBBB + LAFB, especially with hemodynamic instability. Do not “normalize” ST…
Pacemaker Syndrome
Key Points Pacemaker syndrome is a hemodynamic problem caused by loss of proper atrioventricular (AV) synchrony. Most commonly occurs with ventricular pacing that produces retrograde atrial activation, but can also…
Paced Rhythms
Key Points Ventricular pacing changes depolarization, so ST–T segments often look “abnormal.” Expect appropriate discordance: ST/T deflect opposite the main QRS polarity. RV pacing (most common) ≈ LBBB pattern: wide…
Premature Atrial Complexes (PACs)
Key Points PACs are early atrial depolarizations from an ectopic focus that create a premature P wave with a different morphology and axis than the sinus P wave, usually followed…
First-Degree AV Block
Key Points Defined by a PR interval >200 ms with consistent 1:1 AV conduction and no dropped QRS complexes. Conduction delay is most often at the AV node; His–Purkinje delay…
Premature Junctional Complexes (PJCs)
Key Points PJCs are premature impulses from ectopic foci in or near the AV junction. ECG hallmark is a narrow premature beat with an absent or retrograde P wave. Retrograde…
Blocked Premature Atrial Complexes (PACs)
Key Points Definition: early ectopic atrial beats that do not conduct to the ventricles. You see a premature P wave with no following QRS and a pause that is usually…
Premature Complexes (PACs, PJCs, & PVCs) Overview
Key Points: Premature complexes are early depolarizations arising from the atrium, AV junction, or ventricle which interrupt the expected sinus rhythm. Rapid classification by origin: look for a P wave…
Premature Ventricular Complexes (PVCs)
Key Points PVCs are early ventricular depolarizations that produce a wide QRS with secondary ST-T changes and are usually followed by a full compensatory pause. No preceding P wave. A…
ECG Tags
- A-Z
- ACS Mimics
- ACS-OMI
- Activation
- Advanced Level Curriculum
- Annual ECG Competition
- Anterior OMI
- Anterior STEMI
- Approach
- Arrest
- Arrhythmia
- Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy
- Artifact
- ARVC
- ARVD
- Atrial Parasystole
- Attending
- AV Block
- aVF
- aVL
- aVR
- Axis
- Basics
- Board Review
- Bradyarrhythmia
- Chest Pain
- Clumped Beats
- Conduction
- Core
- Core Level Curriculum
- Critical ECG Patterns
- Curriculum
- DDx
- Delta
- Devices
- Diagonal Branch Occlusion
- Differential Diagnoses
- Diffuse ST Elevation
- Documentation
- Early Repolarization
- ECG Interpretation
- ECG Localization
- ECG Variant
- Education/Teaching
- Electrolytes
- Emergencies
- Emergent Cath Lab Activation
- EMS
- Expert Level Curriculum
- Foundations Level Curriculum
- Guidelines
- High-Lateral STEMI
- Hub
- Hyperacute T waves
- Hypercalcemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypermagnesemia
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypokalemia
- Hypomagnesemia
- Hyponatremia
- Hypothermia
- I
- II
- Index
- Inferior OMI
- Inferior STEMI
- Intervals
- Irregular
- Ischemia
- Ischemia & Infarction
- J Waves
- JT
- Juvenile T wave
- LAD Occlusion
- Lateral STEMI
- LBBB
- LCx Occlusion
- Lead Placement
- Life Savers
- LV an
- LV Aneurysm
- Mastery Level Curriculum
- Metabolic
- Mimics
- Morphology
- Narrow QRS
- Occlusion MI
- OMI Pattern
- Orthodromic AVRT
- Osborn Waves
- P Wave
- Paced Rhythms
- Pacemaker/ICD
- Paramedics
- Pauses
- PE
- Pediatrics
- Pericardial
- Pericarditis
- PGY-1
- PGY-2
- PGY-3
- PGY-4
- Post-Cardiac Arrest
- Posterior Extension
- Posterior MI
- Posterior STEMI
- PR
- Preexcitation
- Premature Complexes
- Prolonged QT
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Pulse-Tapping Artifact
- PVCs
- Q Wave
- QRS
- QT
- R Waves
- RAD
- Rate
- RBBB
- RCA Occlusion
- Regular
- Reperfusion
- Rhythm
- RR
- S Waves
- Segments
- Seizure
- Serial ECGs
- Sgarbossa
- Shock
- ST
- ST Depression
- ST Elevation
- STEMI
- STEMI Equivalent
- STEMI Mimics
- STEMI Negative OMI
- Stepwise
- Stroke
- Structural
- Students
- SVT
- Syncope
- T Wave Inversion
- T Waves
- Tachyarrhythmia
- Tachycardia
- Tamponade
- Terminal QRS Distortion
- Toxicology
- TP
- Traditional STEMI Criteria
- U Waves
- Unstable
- V1-V4
- V5
- V6
- Vectors
- Ventricular Repolarization
- Ventricular Rhythms
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Voltage
- Waveforms
- Wide QRS
- Workflow
- WPW