Wide QRS
Results:
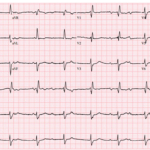
The Syncope ECG With Too Much P
A 68-year-old man has syncope, then has a second syncopal episode while lying still on a stretcher during evaluation at an outpatient clinic. He is sent emergently to the ED….
Preexcitation Pitfalls (Part 4): Potpourri Cases & Final Teaching Points
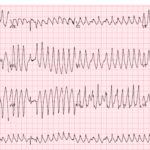
A 49-year-old man arrives with palpitations and chest discomfort. The monitor shows an irregular, wide-complex tachycardia with varying morphology and rates nearing 250 to 300 bpm. The team debates polymorphic…
Preexcitation Pitfalls (Part 3): Wide, Irregular, Fast…Avoid AV Nodal Blockers
A 53-year-old man presents with palpitations and lightheadedness. The following ECG is obtained on arrival and appears very rapid and irregular with changing QRS morphologies. He starts showing signs of…
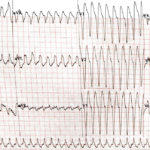
Preexcitation Pitfalls (Part 2): Wide, Regular, Fast…Treat It Like VT
A young man with recurrent palpitations presents to the emergency department hemodynamically stable during an episode. The arrival ECG shows a wide complex, regular tachycardia and the computer interpretation calls…
Appropriate Discordance
Key Points: Appropriate discordance refers to the expected secondary ST segment and T wave pattern seen with abnormal ventricular depolarization, especially LBBB and ventricular-paced rhythm. The ST segment and T…
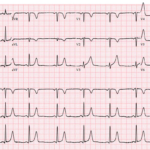
WPW with Antidromic SVT (Antidromic AVRT)
Key Points: Antidromic AVRT is an AV re-entrant tachycardia that conducts antegrade down the accessory pathway and returns retrograde through the AV node (or another pathway), producing a regular wide-complex…
Bidirectional Ventricular Tachycardia (BiVT)
Key Points: BiVT is a regular wide-complex tachycardia with strict beat-to-beat alternation of QRS axis and/or bundle-branch pattern (often an approximately 180° frontal-plane axis flip). In adults, assume digoxin toxicity…
Four ECG Pitfalls That Punish Anchoring Bias
A 43-year-old woman with sharp left-sided chest pain and minimal cardiac risk factors has an initial ECG that is not diagnostic for STEMI. She looks stable, but one feature on…
New RBBB and LAFB (Bifascicular Block) in ACS
Key Points Think proximal LAD / septal ischemia until proven otherwise when a patient with ischemic symptoms develops new RBBB + LAFB, especially with hemodynamic instability. Do not “normalize” ST…
Paced Rhythms
Key Points Ventricular pacing changes depolarization, so ST–T segments often look “abnormal.” Expect appropriate discordance: ST/T deflect opposite the main QRS polarity. RV pacing (most common) ≈ LBBB pattern: wide…
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): Core Overview
Key Points VT is a ventricular-origin rhythm: ≥3 consecutive ventricular beats, QRS >120 ms, rate usually 120–250 bpm. Types include monomorphic VT, polymorphic VT, torsades (PMVT with long QT), ventricular…
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) Mimics
Key Points: Initial Assumption: Any wide (QRS >120 ms), regular tachycardia should be considered ventricular tachycardia (VT) until clearly proven otherwise. VT Characteristics: VT generally has a ventricular rate of…
Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (pVT) Arrest
Key Points Defibrillation First, Minimal Pauses: pVT is rapidly fatal without immediate shocks and high‑quality CPR. Charge defibrillator during compressions and resume compressions immediately after each shock. pVT is a…
Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) Arrest
Key Points Defibrillation First, Minimal Pauses: VF is rapidly fatal without immediate shocks and high‑quality CPR. Charge during compressions and resume compressions immediately after each shock. Chaotic Electrical Activity: VF…
Ventricular Flutter (V-Flutter)
Key Points Definition: A malignant ventricular tachyarrhythmia with a regular, sine-wave–like waveform at ~250–350 bpm, no isoelectric baseline, and no discernible P/QRS/T distinction. Clinical importance: Rapidly degenerates into ventricular fibrillation…
Unstable Bradyarrhythmias
Key Points: Unstable bradyarrhythmias cause poor perfusion which can rapidly progress to shock, irreversible organ injury, or cardiac arrest. Priority: Do not treat the heart rate alone — treat clinical…
Unstable Tachyarrhythmias
Key Points: Intervene Immediately: Unstable tachyarrhythmias pose significant risk for rapid clinical deterioration that may lead to irreversible end-organ damage or cardiac arrest. Clinical Indicators of Instability: Altered Mental Status:…
Premature Complexes (PACs, PJCs, & PVCs) Overview
Key Points: Premature complexes are early depolarizations arising from the atrium, AV junction, or ventricle which interrupt the expected sinus rhythm. Rapid classification by origin: look for a P wave…
Osborn (J) Wave: Basics
Key Points An Osborn wave is a notch or slur at the J point that becomes more prominent as core temperature falls. Most visible in inferolateral and precordial leads; can…
Premature Ventricular Complexes (PVCs)
Key Points PVCs are early ventricular depolarizations that produce a wide QRS with secondary ST-T changes and are usually followed by a full compensatory pause. No preceding P wave. A…
ECG Tags
- A-Z
- ACS Mimics
- ACS-OMI
- Activation
- Advanced Level Curriculum
- Annual ECG Competition
- Anterior OMI
- Anterior STEMI
- Approach
- Arrest
- Arrhythmia
- Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy
- Artifact
- ARVC
- ARVD
- Atrial Parasystole
- Attending
- AV Block
- aVF
- aVL
- aVR
- Axis
- Basics
- Board Review
- Bradyarrhythmia
- Chest Pain
- Clumped Beats
- Conduction
- Core
- Core Level Curriculum
- Critical ECG Patterns
- Curriculum
- DDx
- Delta
- Devices
- Diagonal Branch Occlusion
- Differential Diagnoses
- Diffuse ST Elevation
- Documentation
- Early Repolarization
- ECG Interpretation
- ECG Localization
- ECG Variant
- Education/Teaching
- Electrolytes
- Emergencies
- Emergent Cath Lab Activation
- EMS
- Expert Level Curriculum
- Foundations Level Curriculum
- Guidelines
- High-Lateral STEMI
- Hub
- Hyperacute T waves
- Hypercalcemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypermagnesemia
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypokalemia
- Hypomagnesemia
- Hyponatremia
- Hypothermia
- I
- II
- Index
- Inferior OMI
- Inferior STEMI
- Intervals
- Irregular
- Ischemia
- Ischemia & Infarction
- J Waves
- JT
- Juvenile T wave
- LAD Occlusion
- Lateral STEMI
- LBBB
- LCx Occlusion
- Lead Placement
- Life Savers
- LV an
- LV Aneurysm
- Mastery Level Curriculum
- Metabolic
- Mimics
- Morphology
- Narrow QRS
- Occlusion MI
- OMI Pattern
- Orthodromic AVRT
- Osborn Waves
- P Wave
- Paced Rhythms
- Pacemaker/ICD
- Paramedics
- Pauses
- PE
- Pediatrics
- Pericardial
- Pericarditis
- PGY-1
- PGY-2
- PGY-3
- PGY-4
- Post-Cardiac Arrest
- Posterior Extension
- Posterior MI
- Posterior STEMI
- PR
- Preexcitation
- Premature Complexes
- Prolonged QT
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Pulse-Tapping Artifact
- PVCs
- Q Wave
- QRS
- QT
- R Waves
- RAD
- Rate
- RBBB
- RCA Occlusion
- Regular
- Reperfusion
- Rhythm
- RR
- S Waves
- Segments
- Seizure
- Serial ECGs
- Sgarbossa
- Shock
- ST
- ST Depression
- ST Elevation
- STEMI
- STEMI Equivalent
- STEMI Mimics
- STEMI Negative OMI
- Stepwise
- Stroke
- Structural
- Students
- SVT
- Syncope
- T Wave Inversion
- T Waves
- Tachyarrhythmia
- Tachycardia
- Tamponade
- Terminal QRS Distortion
- Toxicology
- TP
- Traditional STEMI Criteria
- U Waves
- Unstable
- V1-V4
- V5
- V6
- Vectors
- Ventricular Repolarization
- Ventricular Rhythms
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Voltage
- Waveforms
- Wide QRS
- Workflow
- WPW