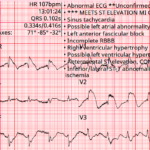
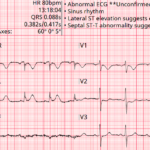
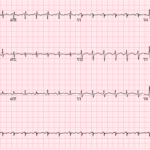
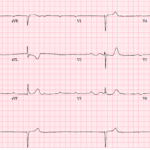
AV Block
Results:
Baltimore City EMS ECGs: Pitfalls and Mimics (Part 2)
A 54-year-old man presents to the emergency department by EMS with acute shortness of breath. A prehospital ECG triggers a STEMI alert based on the computer interpretation. The tracing shows…
Baltimore City EMS ECGs: Pitfalls and Mimics (Part 1)
A 68-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by EMS with acute chest discomfort. The following prehospital ECG was obtained and shows concave ST elevation across multiple leads. The…
Three More ECG Pitfalls That Punish Anchoring Bias
A 51-year-old man with lung cancer presents with shortness of breath and tachycardia. The arrival ECG shows an S1Q3 pattern and seems to support a familiar diagnosis that would normally…
Dr. Mattu’s 5 Favorite ECG Cases of 2025
A 68-year-old man presents after syncope with profound bradycardia. The ECG shows a very slow ventricular rate with high-grade AV block. The reflex move is to focus only on pacing,…
First-Degree AV Block
Key Points Defined by a PR interval >200 ms with consistent 1:1 AV conduction and no dropped QRS complexes. Conduction delay is most often at the AV node; His–Purkinje delay…
Atrioventricular Blocks (AVB): Comprehensive Summary
Key Points AV block specifically reflects delayed or failed impulse conduction from atria to ventricles. Classification of blocks depend on the location of conduction delay or block within the cardiac…
Grouped Beats: A Subtle AV Block Pitfall
An elderly patient is brought to the emergency department with acute stroke symptoms and the following routine 12-lead ECG is obtained during the patient’s stroke evaluation:
Isorhythmic AV Dissociation
Key Points Definition: A type of AV dissociation in which sinus and escape rates are nearly identical, so P waves and QRS complexes appear to “track” each other while remaining unrelated….
Third-Degree AV Block (Complete Heart Block)
Key Points: Definition: Third-degree AV block is complete failure of conduction from atria to ventricles, resulting in independent atrial and ventricular activity—known as AV dissociation. Hallmark Feature: No P waves…
High-Grade (Advanced) AV Block
Key Points Definition: A severe form of second-degree AV block with two or more consecutive non‑conducted P waves (for example 3:1, 4:1). Do not force a Mobitz label when multiple…
Second-Degree AV Block Type I (Mobitz I/Wenckebach)
Key Points: Definition: Progressive PR interval prolongation until one atrial impulse fails to conduct to the ventricles (P wave is non-conducted), after which the cycle repeats. Site of Block: Typically…
Second-Degree AV Block with 2:1 Conduction
Key Points: Definition: A form of second-degree AV block in which every other atrial impulse is blocked, producing a 2:1 atrioventricular conduction ratio. Typing Limitation: Differentiating between Mobitz I and…
Second-Degree AV Block Type II (Mobitz II)
Key Points Definition: Sudden failure of AV conduction after at least two consecutive conducted beats with identical PR intervals, followed by a single non‑conducted P wave. Sinus rate: P–P interval…
Bifascicular Block
Key Points Definition: Conduction block in any two of the three fascicles: right bundle branch (RBB), left anterior fascicle (LAF), or left posterior fascicle (LPF). High-Risk OMI Pattern: New RBBB…
Rhythm Interpretation: differential diagnoses for electrocardiographic polyuria in unstable bradycardias
An 88-year-old man is brought into the ED with lightheadedness and palpitations. The following ECG is obtained:
Bradyarrhythmias: differentiation of Mobitz and other atrioventricular (AV) blocks
An 83-year-old woman is brought into the ED with lightheadedness and is noted to be bradycardic. The following ECG is obtained:
Bifascicular blocks, BRASH syndrome, and so much more!
This week we will continue discussing 6 more interesting prehospital EMS ECGs. Let’s start with this 78-year-old woman with PMHx of HTN who called an ambulance for generalized weakness associated…
How to distingusish between left anterior vs. posterior fascicular blocks (LAFB vs. LPFB), hyperkalemia emergencies, and much more!
This week we will quickly review 6 interesting prehospital EMS ECGs. Let’s start with this 46-year-old man who called an ambulance for chest pain and was noted to be diaphoretic….
AV Block Bootcamp (Episode 3/3): the answer lies in the PR interval!
HPI: A 72-year-old female presents to the ED with chest pain and lightheadedness. The following ECG is obtained:
AV Block Bootcamp (Episode 2/3): what is the atrium doing, what is the ventricle doing, and what is their relationship?
A 72-year-old female presents to the ED with dyspnea. The following ECG is obtained:
ECG Tags
- A-Z
- ACS Mimics
- ACS-OMI
- Activation
- Advanced Level Curriculum
- Annual ECG Competition
- Anterior OMI
- Anterior STEMI
- Approach
- Arrest
- Arrhythmia
- Artifact
- Attending
- AV Block
- aVF
- aVL
- aVR
- Axis
- Basics
- Board Review
- Bradyarrhythmia
- Chest Pain
- Clumped Beats
- Conduction
- Core
- Core Level Curriculum
- Critical ECG Patterns
- Curriculum
- DDx
- Delta
- Devices
- Diagonal Branch Occlusion
- Differential Diagnoses
- Diffuse ST Elevation
- Documentation
- Early Repolarization
- ECG Interpretation
- ECG Localization
- ECG Variant
- Education/Teaching
- Electrolytes
- Emergencies
- Emergent Cath Lab Activation
- EMS
- Expert Level Curriculum
- Foundations Level Curriculum
- Guidelines
- High-Lateral STEMI
- Hub
- Hyperacute T waves
- Hypercalcemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypermagnesemia
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypokalemia
- Hyponatremia
- Hypothermia
- I
- II
- Index
- Inferior OMI
- Inferior STEMI
- Intervals
- Irregular
- Ischemia
- Ischemia & Infarction
- J Waves
- JT
- LAD Occlusion
- Lateral STEMI
- LBBB
- LCx Occlusion
- Lead Placement
- Life Savers
- LV an
- LV Aneurysm
- Mastery Level Curriculum
- Metabolic
- Mimics
- Narrow QRS
- Occlusion MI
- OMI Pattern
- Orthodromic AVRT
- Osborn Waves
- P Wave
- Paced Rhythms
- Pacemaker/ICD
- Paramedics
- Pauses
- PE
- Pediatrics
- Pericardial
- Pericarditis
- PGY-1
- PGY-2
- PGY-3
- PGY-4
- Post-Cardiac Arrest
- Posterior Extension
- Posterior MI
- Posterior STEMI
- PR
- Preexcitation
- Premature Complexes
- Prolonged QT
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Pulse-Tapping Artifact
- PVCs
- Q Wave
- QRS
- QT
- R Waves
- RAD
- Rate
- RBBB
- RCA Occlusion
- Regular
- Reperfusion
- Rhythm
- RR
- S Waves
- Segments
- Seizure
- Serial ECGs
- Shock
- ST
- ST Depression
- ST Elevation
- STEMI
- STEMI Equivalent
- STEMI Mimics
- STEMI Negative OMI
- Stepwise
- Stroke
- Structural
- Students
- SVT
- Syncope
- T Waves
- Tachyarrhythmia
- Tachycardia
- Tamponade
- Terminal QRS Distortion
- Toxicology
- TP
- Traditional STEMI Criteria
- U Waves
- Unstable
- V1-V4
- V5
- V6
- Vectors
- Ventricular Repolarization
- Ventricular Rhythms
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Voltage
- Waveforms
- Wide QRS
- Workflow
- WPW