ECG Interpretation
Results:
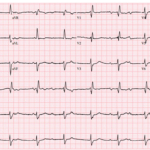
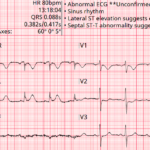
The Syncope ECG With Too Much P
A 68-year-old man has syncope, then has a second syncopal episode while lying still on a stretcher during evaluation at an outpatient clinic. He is sent emergently to the ED….
T Wave Inversion in V1-V3: DDx
Key Points: Anterior T wave inversion in V1-V3 is not synonymous with “anteroseptal ischemia.” The differential includes ACS, right heart strain, conduction/structural disease, and normal variants. In acute care, the…
Preexcitation Pitfalls (Part 4): Potpourri Cases & Final Teaching Points
A 49-year-old man arrives with palpitations and chest discomfort. The monitor shows an irregular, wide-complex tachycardia with varying morphology and rates nearing 250 to 300 bpm. The team debates polymorphic…
QRS Morphology and ST-T Interpretation: Basics
Key Points: Read the QRS before you read the ST segment or T wave. Ventricular depolarization shapes repolarization. Narrow QRS usually reflects normal His-Purkinje conduction. Wide QRS suggests abnormal ventricular…
Preexcitation Syndromes: Overview
Key Points: Pre-excitation means an accessory pathway allows atrial impulses to reach the ventricle without traversing the AV node, producing early ventricular activation. A delta wave is the defining ECG…
The Life Savers: Critical ECG Pattern Hub
Key Points: Critical ECG patterns represent time-sensitive, life-threatening cardiac or systemic conditions that demand immediate recognition to prevent death or irreversible organ injury. These are the “can’t-miss” ECGs. Use this…
Stepwise Approach to STAT ECGs Hub
Key Points: Consistency saves lives: Use a repeatable ECG routine to reduce misses in chaotic settings. Many valid methods exist. Pick an order that fits your acute-care workflow and do…
P Wave: Basics
Key Points: Definition and measurement: The P wave is atrial depolarization. Measure duration from initial deflection to return to baseline and amplitude from baseline to peak. Normal values: Duration <120…
Baltimore City EMS ECGs: Pitfalls and Mimics (Part 1)
A 68-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by EMS with acute chest discomfort. The following prehospital ECG was obtained and shows concave ST elevation across multiple leads. The…
QT Interval: Basics
Key Points: Definition: QT is measured from QRS onset to T-wave end. It reflects total ventricular depolarization plus repolarization. Use QTc: QT varies with heart rate. Interpret QTc, not the…
Waveforms, Segments, & Intervals: Basics
Key Points: Every ECG tracing is built from waveforms (deflections), segments (baseline portions between waveforms), and intervals (time that include waveforms plus segments). Waveforms describe electrical events (depolarization or repolarization)….
Short QT Interval: DDx
Key Points: Short QT Interval: A QT interval is considered short when the corrected QT (QTc) interval is less than 350 ms. A short QT interval on the ECG can…
ECG STAT Curriculum Hub
Why ECG Interpretation Matters: The ECG is one of the fastest, highest-impact diagnostic tests in acute care. When interpretation is rapid and accurate, patients get timely reperfusion, pacing, defibrillation, antidotes,…
ECG Findings of LV Aneurysm
Key Points: Definition: A true LV aneurysm is a chronic, post transmural MI complication from scarred myocardium with akinetic or dyskinetic (paradoxical) wall motion. ECG hallmark: Persistent ST elevation in…
Post-Thrombolytic Reperfusion ECG Findings
Key Points Reperfusion after fibrinolysis is a bedside diagnosis using a bundle of findings: symptoms, ECG trend, and hemodynamic/electrical stability. Best ECG marker of successful fibrinolysis: at least 50% ST-segment…
ECG Evidence of Reperfusion After Occlusion
Key Points Reperfusion and re-occlusion can occur spontaneously or after therapy. The ECG often reflects these changes earlier than symptoms. Most useful bedside ECG marker of reperfusion is ST-segment resolution…
Pulse-Tapping Artifact
Key Points: Mechanical artifact caused by an ECG electrode sitting on top of a strong arterial pulse. Seen frequently in dialysis patients with AV fistulas. Can mimic serious pathology including…
Pediatric ECG Red Flags
Key Points Any wide QRS (>90 ms) in an infant or small child is abnormal and should trigger evaluation for VT, sodium-channel blockade, or conduction disease. QTc >450 ms in…
Pediatric ECG in Cardiac Arrest
Key Points ECG rhythms in pediatric arrest differ from adults. Pulseless arrest in children is most often asphyxial, but ECG clues can reveal reversible metabolic, toxicologic, or structural causes. Wide…
Pediatric ECG: Basics
Key Points Pediatric ECGs are not scaled-down adult ECGs. Right axis deviation, large R waves in V1, and T wave inversions in V1 to V3 are expected in healthy children….
ECG Tags
- A-Z
- ACS Mimics
- ACS-OMI
- Activation
- Advanced Level Curriculum
- Annual ECG Competition
- Anterior OMI
- Anterior STEMI
- Approach
- Arrest
- Arrhythmia
- Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy
- Artifact
- ARVC
- ARVD
- Atrial Parasystole
- Attending
- AV Block
- aVF
- aVL
- aVR
- Axis
- Basics
- Board Review
- Bradyarrhythmia
- Chest Pain
- Clumped Beats
- Conduction
- Core
- Core Level Curriculum
- Critical ECG Patterns
- Curriculum
- DDx
- Delta
- Devices
- Diagonal Branch Occlusion
- Differential Diagnoses
- Diffuse ST Elevation
- Documentation
- Early Repolarization
- ECG Interpretation
- ECG Localization
- ECG Variant
- Education/Teaching
- Electrolytes
- Emergencies
- Emergent Cath Lab Activation
- EMS
- Expert Level Curriculum
- Foundations Level Curriculum
- Guidelines
- High-Lateral STEMI
- Hub
- Hyperacute T waves
- Hypercalcemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypermagnesemia
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypokalemia
- Hypomagnesemia
- Hyponatremia
- Hypothermia
- I
- II
- Index
- Inferior OMI
- Inferior STEMI
- Intervals
- Irregular
- Ischemia
- Ischemia & Infarction
- J Waves
- JT
- Juvenile T wave
- LAD Occlusion
- Lateral STEMI
- LBBB
- LCx Occlusion
- Lead Placement
- Life Savers
- LV an
- LV Aneurysm
- Mastery Level Curriculum
- Metabolic
- Mimics
- Morphology
- Narrow QRS
- Occlusion MI
- OMI Pattern
- Orthodromic AVRT
- Osborn Waves
- P Wave
- Paced Rhythms
- Pacemaker/ICD
- Paramedics
- Pauses
- PE
- Pediatrics
- Pericardial
- Pericarditis
- PGY-1
- PGY-2
- PGY-3
- PGY-4
- Post-Cardiac Arrest
- Posterior Extension
- Posterior MI
- Posterior STEMI
- PR
- Preexcitation
- Premature Complexes
- Prolonged QT
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Pulse-Tapping Artifact
- PVCs
- Q Wave
- QRS
- QT
- R Waves
- RAD
- Rate
- RBBB
- RCA Occlusion
- Regular
- Reperfusion
- Rhythm
- RR
- S Waves
- Segments
- Seizure
- Serial ECGs
- Sgarbossa
- Shock
- ST
- ST Depression
- ST Elevation
- STEMI
- STEMI Equivalent
- STEMI Mimics
- STEMI Negative OMI
- Stepwise
- Stroke
- Structural
- Students
- SVT
- Syncope
- T Wave Inversion
- T Waves
- Tachyarrhythmia
- Tachycardia
- Tamponade
- Terminal QRS Distortion
- Toxicology
- TP
- Traditional STEMI Criteria
- U Waves
- Unstable
- V1-V4
- V5
- V6
- Vectors
- Ventricular Repolarization
- Ventricular Rhythms
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Voltage
- Waveforms
- Wide QRS
- Workflow
- WPW