Syncope
Results:
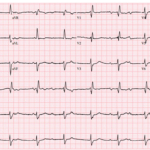
The Syncope ECG With Too Much P
A 68-year-old man has syncope, then has a second syncopal episode while lying still on a stretcher during evaluation at an outpatient clinic. He is sent emergently to the ED….
Three More ECG Pitfalls That Punish Anchoring Bias
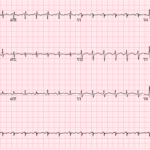
A 51-year-old man with lung cancer presents with shortness of breath and tachycardia. The arrival ECG shows an S1Q3 pattern and seems to support a familiar diagnosis that would normally…
Short QT Interval: DDx
Key Points: Short QT Interval: A QT interval is considered short when the corrected QT (QTc) interval is less than 350 ms. A short QT interval on the ECG can…
Dr. Mattu’s 5 Favorite ECG Cases of 2025
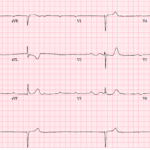
A 68-year-old man presents after syncope with profound bradycardia. The ECG shows a very slow ventricular rate with high-grade AV block. The reflex move is to focus only on pacing,…
Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy (ACM)
Key Points: Definition & Terminology: Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy (ACM), previously known as Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy/Dysplasia (ARVC/D), is an inherited disorder characterized by progressive fibrofatty replacement of the ventricular myocardium, predominantly…
Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy (HOCM)
Key Points Definition and mechanics: Genetic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with asymmetric LV hypertrophy, typically septal, causing dynamic LVOT obstruction from systolic anterior motion (SAM) of the mitral valve. Gradient worsens when…
Yamaguchi Pattern: Apical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (ApHCM)
Key Points Definition and mechanics: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy variant with maximal hypertrophy at the LV apex (apical HCM, ApHCM). LVOT is often not obstructed at rest; some patients have mid-ventricular obstruction…
Syncope Emergencies
Key Points: ECG and monitor early: First-time seizure, near-syncope, unexplained LOC, or syncope all get a 12-lead now and continuous telemetry. Repeat ECG during symptoms or after another event. History…
Must-Know Syncope: DDx
Key Points: Syncope and the ECG: Syncope is a transient loss of consciousness and postural tone, characterized by rapid onset, brief duration, and spontaneous recovery without medical intervention. Cardiac syncope…
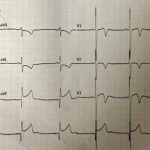
Not Your Usual STEMI: High Voltage and Narrow Q Waves
A 16-year-old male is referred to the emergency department from a primary care clinic with concern for STEMI. He has no known past medical history. At the clinic, he reported…
Epsilon Waves
Key Points Definition: Small, low-amplitude positive deflections at the terminal QRS or very early ST segment, caused by delayed right ventricular activation through diseased myocardium. Association: Highly specific for arrhythmogenic…
Short QT Syndrome
Key Points Short QT Syndrome (SQTS) is a rare condition characterized by a shortened QT interval on the ECG, increasing the risk of atrial and ventricular arrhythmias, including sudden cardiac…
QRS Fragmentation (fQRS)
Key Points Definition: QRS fragmentation (fQRS) refers to the presence of additional notches or spikes within the QRS complex, observed in at least two contiguous leads corresponding to a specific…
Congenital Long QT Syndrome
Key Points Congenital Long QT Syndrome (LQTS) is a group of genetic disorders characterized by a prolonged QT interval on ECG, leading to an increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias and…
Acquired Long QT Syndrome
Key Points Acquired Long QT Syndrome (LQTS) is the most common form of LQTS, resulting from medications, electrolyte disturbances, or underlying medical conditions. High-risk factors include the use of multiple…
Brugada Syndrome (BrS)
Key Points: Life-Threatening Sodium Channelopathy: Predisposes to ventricular arrhythmias (VF/VT) and sudden cardiac death (SCD), often in otherwise “healthy” hearts. When to Suspect BrS: Patients with syncope, unexplained “seizures,” ventricular…
Literature Review: Brugada Syndrome
A 55-year-old man with no significant PMHx (on no medications) presents to the emergency department with right lower quadrant pain. He is afebrile on arrival, with mild sinus tachycardia. He…
Literature Review: Fever and ST segment elevation after syncope
A young woman presents to the ED after a syncopal episode. She hit her chest after falling and has reproducible chest wall tenderness on exam. She is also noted to…
Literature Review: ST segment elevation after syncope and cardiac arrest
A 22-year-old man with no known significant PMHx presents after syncope. He is asymptomatic on arrival with normal vital signs. History and physical exam is non-diagnostic. While an ECG is…
Differential Diagnoses: what to consider in patients who have isolated syncope and present asymptomatic
A 26-year-old woman presents to the ED after 2 episodes of lightheadedness and near syncope that lasted 30-60 seconds each. She is now asymptomatic with normal vital signs and a…
ECG Tags
- A-Z
- ACS Mimics
- ACS-OMI
- Activation
- Advanced Level Curriculum
- Annual ECG Competition
- Anterior OMI
- Anterior STEMI
- Approach
- Arrest
- Arrhythmia
- Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy
- Artifact
- ARVC
- ARVD
- Atrial Parasystole
- Attending
- AV Block
- aVF
- aVL
- aVR
- Axis
- Basics
- Board Review
- Bradyarrhythmia
- Chest Pain
- Clumped Beats
- Conduction
- Core
- Core Level Curriculum
- Critical ECG Patterns
- Curriculum
- DDx
- Delta
- Devices
- Diagonal Branch Occlusion
- Differential Diagnoses
- Diffuse ST Elevation
- Documentation
- Early Repolarization
- ECG Interpretation
- ECG Localization
- ECG Variant
- Education/Teaching
- Electrolytes
- Emergencies
- Emergent Cath Lab Activation
- EMS
- Expert Level Curriculum
- Foundations Level Curriculum
- Guidelines
- High-Lateral STEMI
- Hub
- Hyperacute T waves
- Hypercalcemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypermagnesemia
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypokalemia
- Hypomagnesemia
- Hyponatremia
- Hypothermia
- I
- II
- Index
- Inferior OMI
- Inferior STEMI
- Intervals
- Irregular
- Ischemia
- Ischemia & Infarction
- J Waves
- JT
- Juvenile T wave
- LAD Occlusion
- Lateral STEMI
- LBBB
- LCx Occlusion
- Lead Placement
- Life Savers
- LV an
- LV Aneurysm
- Mastery Level Curriculum
- Metabolic
- Mimics
- Morphology
- Narrow QRS
- Occlusion MI
- OMI Pattern
- Orthodromic AVRT
- Osborn Waves
- P Wave
- Paced Rhythms
- Pacemaker/ICD
- Paramedics
- Pauses
- PE
- Pediatrics
- Pericardial
- Pericarditis
- PGY-1
- PGY-2
- PGY-3
- PGY-4
- Post-Cardiac Arrest
- Posterior Extension
- Posterior MI
- Posterior STEMI
- PR
- Preexcitation
- Premature Complexes
- Prolonged QT
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Pulse-Tapping Artifact
- PVCs
- Q Wave
- QRS
- QT
- R Waves
- RAD
- Rate
- RBBB
- RCA Occlusion
- Regular
- Reperfusion
- Rhythm
- RR
- S Waves
- Segments
- Seizure
- Serial ECGs
- Sgarbossa
- Shock
- ST
- ST Depression
- ST Elevation
- STEMI
- STEMI Equivalent
- STEMI Mimics
- STEMI Negative OMI
- Stepwise
- Stroke
- Structural
- Students
- SVT
- Syncope
- T Wave Inversion
- T Waves
- Tachyarrhythmia
- Tachycardia
- Tamponade
- Terminal QRS Distortion
- Toxicology
- TP
- Traditional STEMI Criteria
- U Waves
- Unstable
- V1-V4
- V5
- V6
- Vectors
- Ventricular Repolarization
- Ventricular Rhythms
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Voltage
- Waveforms
- Wide QRS
- Workflow
- WPW